BEEGENETICS
Analysis of the genetic composition of bee colonies
As part of projects to manage the genetic diversity of bee populations – conservatories, genomic selection programs – APINOV proposes an evaluation of bee subspecies (or breeds) by DNA analysis.
These analyses are performed by an original method of microarray genotyping. They make it possible to determine precisely the genetic composition of a bee colony, integrating the proportions of each subspecies and the genetic diversity.
The identification of bee breeds
- biometric analyses, based on morphological characteristics, such as the length of the tongue, the coloration of the abdomen, hair, ulnar index, etc.
- genetic analysis, based on genetic information contained in DNA
Among DNA analyses, the study of the mitochondrial genome is the simplest and the least expensive because the analysis of a single worker informs us about the genotype of the queen (mitochondria being transmitted exclusively and entirely by the mother). Nevertheless, this information does not allow to see the impact of males on the worker genotype. Thus, mitochondrial DNA only gives a partial determination of the breed.
Conversely, the study of nuclear DNA indicates the genotype of the queen and the males that fertilized it (the nucleus of the cells being transmitted to the workers by the mother and father). The analysis of a certain number of worker bees of the same colony (variable number according to the techniques) makes it possible to obtain a more complete information on the genetics of the colony.
Principle of genotyping on microarray
Microarray technology is a methodological innovation that uses the principle of comparative genomic hybridization. It is based on the ability of denatured DNA (single strand) to spontaneously reform its double helix in the presence of a complementary strand (hybridization property).
The innovative method developed by Labogena consists in hybridizing the DNA of a mixture of workers (target DNA) on a network of DNA sequences (probes) fixed on a DNA chip. Each target DNA strand will then hybridize with probes that are complementary to it to form a probe/target duplex. Through fluorescence marking of the target DNA, it is then possible to reveal, for each probe, whether there has been hybridization and to obtain the genetic signature of the sample studied.
In this case, it involves comparing the DNA of a sample of bees to be studied with DNA sequences characteristic of the different subspecies of bees. The bee-specific genotyping chip now includes 1750 molecular markers. It comes from the BeeStrong project, piloted by LABOGENA, in partnership with ITSAP and INRAE, and funded by FranceAgriMer.
Microarray genotyping gives us very precise information on the genetic composition of bee colonies.
What results are achieved ?
Hover over each result to explore the analysis.

The genetic composition of your colonies
Genetic composition
The Beegenetics analysis bulletin includes, for each colony, the proportions of each identified subspecies (Mellifera, Ligustica, Caucasia, etc.) of the queen. This composition is estimated from a reconstruction of the genotype of the queen.

The genetic diversity of your colonies
Genetic diversity
The Beegenetics analysis also gives information on the genetic diversity of each colony, between 0 and 1, compared to the colonies constituting the database. This information provides information on the diversity of genes, including within the same subspecies.

The appearance between your colonies
Apparent between colonies
Beegenetics results include an apparent tree that indicates the genetic distance between your different analyzed colonies. In this tree, the closer the colonies are and their branches are short, the more they are related so genetically close.
Download above the order form and send us the part “Request analysis” accompanied by your proof of payment.
Examples of applications
These analyses may be useful for :
The creation and monitoring of conservatories
In the context of a black bee conservatory, for example, Beegenetics analyses allow you to verify that the colonies are mainly composed of bees of the subspecies Mellifera and leave the conservatory queens too introgressed or with too little genetic diversity. In case of breeding on the conservatory, Beegenetics analyses also allow you to perform crosses from queens with the most distant appearance in order to maintain maximum genetic diversity.
Conservatoire d'abeilles noires
Colas Carrière Cozzi - Norrante (04)

Genetic selection programmes
As part of a genetic selection program, Beegenetics analyses allow you to graft on queens that have a high genetic diversity and make crosses between genetically distant lines.
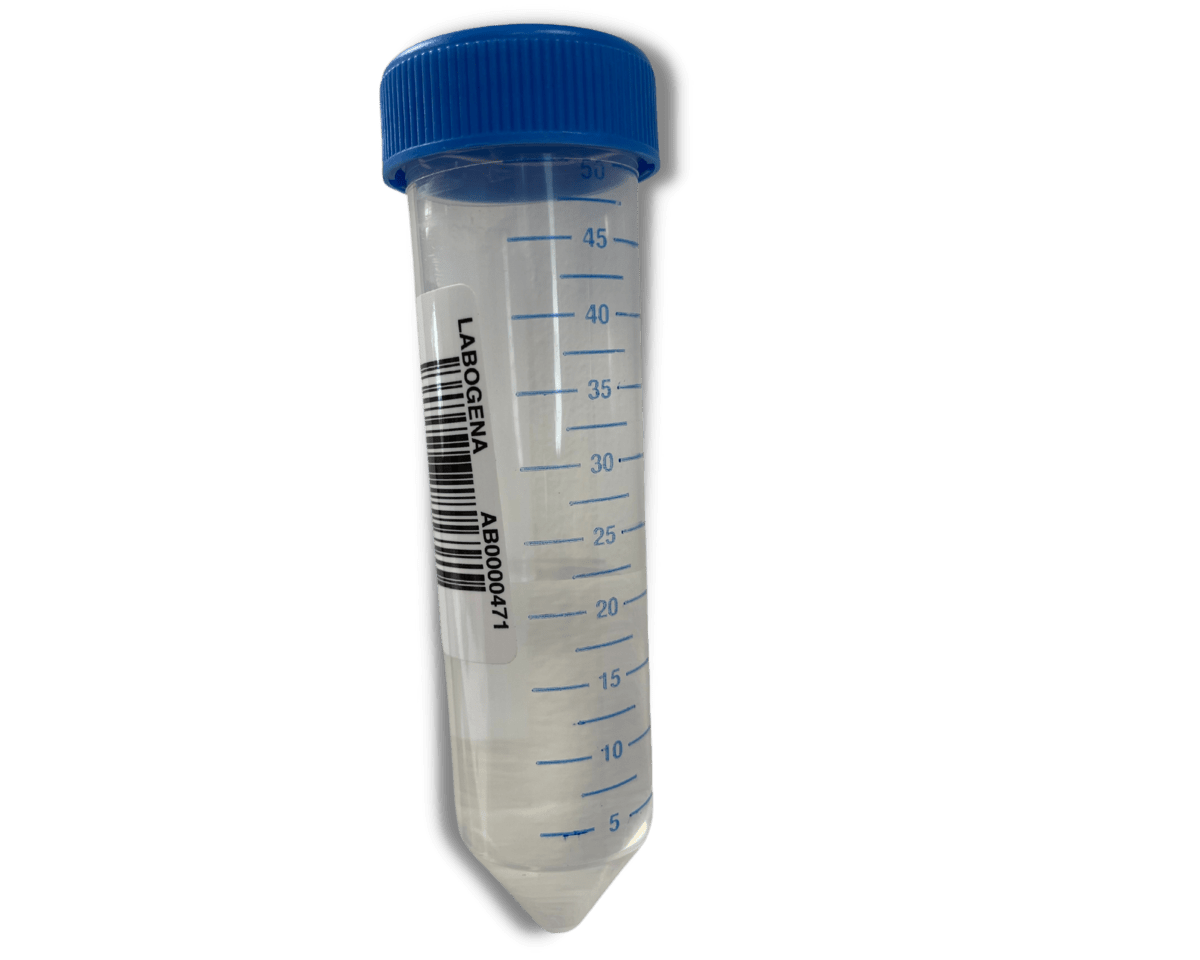

How to perform sampling?
The sampling method is very simple. If you wish to carry out analyses, we will send you tubes containing a buffer solution (1 tube per colony).
You will only have to put about twenty bees per colony and send us the tubes.
Prices (Metropolitan France) and delays
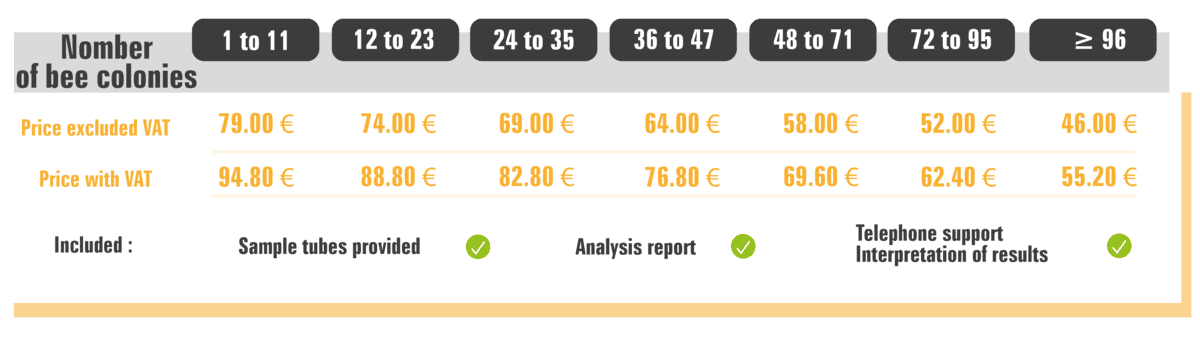
The rate is indicated for an analysis, that is, for a colony. It includes the sending of the sampling tubes, the analysis report and the telephone support for the interpretation of the results. Regarding the deadlines, if you opt for the analysis of a complete batch, which is equivalent to 96 colonies or 1 DNA chip (or multiples thereof), the results will be ready within 4 weeks. If you plan to do fewer than 96 analyses, you will receive your results in the fall, as this will allow us to consolidate requests from multiple clients and complete bullets accordingly.
We can also offer a sampling service by our technicians and consulting services for the creation of conservatories or as part of genetic selection programs (on quote).

